Features and Benefits
![]()
E-MAX underwent extensive laboratory evaluations, including wear simulator testing.
Excellent Wear Properties
The crosslinking density of E-MAX for knee was fine-tuned to be about the same as 7 Mrad XLPE and has demonstrated very low wear in hip simulator testing: 74% less wear than conventional polyethylene.[1]
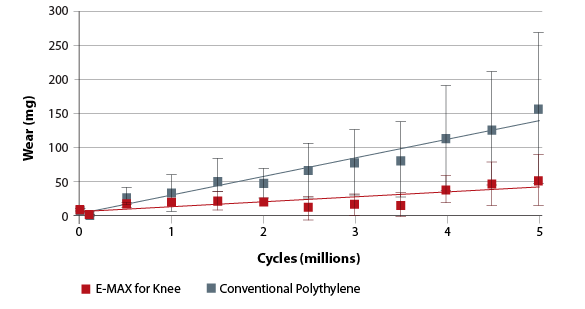
Knee Simulator Wear. Largest available size.
Oxidative Stability under Harsh Testing Conditions
The mechanical anneal eliminates free radicals to near the detection threshold of testing equipment (ESR). [2,3] After accelerated aging the E-MAX showed minimal change in free radical content, indicating that the Vitamin E stabilized the free radicals, preventing them from reacting with oxygen. [4] To further test oxidation resistance under extreme conditions, samples were exhaustively extracted to remove as much Vitamin E as possible, and then subjected to accelerated aging. Even under extreme conditions, no positive oxidation index was measured in E-MAX. [4]
Evenly Distributed Vitamin E
Chemical analysis demonstrated that the Vitamin E is profile is constant throughout E-MAX, indicating that it is evenly distributed throughout the material. [4] This is because vitamin E is blended with UHMWPE powder before creating the UHMWPE barstock. In contrast, materials into which the vitamin E is diffused after UHMWPE consolidation (e.g. Biomet E1), result in more concentrated levels of vitamin E near the surface.
- University of Nebraska Medical Center. An in-vitro wear durability study of the A200 CR Knee System: two sizes and two bearing materials.Test report dated November 11, 2011. On file with KYOCERA Medical Technologies, Inc.
- Materials Characterization testing. Test report TP0322. On file with KYOCERA Medical Technologies, Inc.
- Bhattacharyya S, Matrisciano L, Spiegelberg S, Harris W, Muratoglu O. Mechanical elimination of residual free radicals in an irradiated UHMWPE rod: advantages over melting. 50th annual meeting of the orthopaedic research society. 2004:1474.
- Cambridge Polymer Group. Analysis of CIMA and E-CIMA Material. Test report dated July 15, 2011. On file with KYOCERA Medical Technologies, Inc.